Chemical reactions and equations
→The process in which new substances with new properties are formed from one or more substance is called
chemical reaction.
•The substances which take part in chemical reaction are called reactants.
•The substances which are formed in a chemical reaction are called Products.
Examples:-
(I)Digestion of food
(II)Respiration
(III)Rusting of iron
(IV)Burning of magnesium ribbon
(V)Formation of curd
Chemical reaction involves:
•change in state
•change in colour
•change in temperature
•Evolution of gas
→chemical Equation
•A chemical reation can be represented by chemical equation.It involves used of symbol of elements or chemical formula of reactants and product with mention of physical state.
•The necessary conditions such as temperature, pressure or any catalyst should be written on arrow between reactant and products.eg magnesium is burnt in air to form magnesium oxide.
Mg +o²→ Mgo
Balancing chemical equations
•law of conservation of Mass:Matter can neither be create be destroyed in a chemical reaction.
•So number of elements involved in chemical reaction should remain same at reactant and product side.
Stepwise balancing (hit and trial)
Step 1.write a chemical equation and draw boxes around each formula.
Fe+H²O→Fe³O⁴+H²
•Do not change anything inside the box.
Step 2.Conunt the number of atoms of each element on both sides of chemical equation.
Element No of atom at reatantside
Fe 1
H 2
O 1
→No of atoms of product side
3
2
4
Step 3.Equalise the number of atoms of element which has maximum number by putting in front of it.
Fe+4H²O→Fe³O⁴ +H²
Step 4.Try to equalize all the atoms of elements on reactant and product side by adding coefficient in front of it.
3Fe + 4H²O→Fe³0⁴ +4H²
•Now all the atoms of elements are equal on both sides.
Step 5.write the physical states of reactants and products.
3Fe(s)+4H²O(g)→Fe³O⁴(s)+4H²(g)
Solid State=(s)
Liquid state=(l)
Gaseous state=(g)
Aqueous state=(aq)
Step 6.write necessary conditions of temperature, Pressure or catalyst on arrow above or below.
Chemical equation definition:
Combination Reaction:The reaction in which two or more reactant combine to form a single product.
E.g (i) Burning of coal
C (s) +O²(g)→Co²(g)
(ii) Formation of water
2H²(g)+o²(g)→2H²O(l)
(iii) CaO(s)+H²O(l)→Ca(OH)² (aq)
(Quick lime) (slaked lime)
Exothermic Reaction:Reaction in which heat is released along with formation of products.
Eg (i) Burning of natural gas
CH⁴(g)+0²(g)→Co²(g)+2H²0(g)+heat
(ii)Respiration is also an exothermic reaction.
C6 H¹²O6(aq)+6O²(g)→6Co²(aq)+6H²O (l)+energy
Decomposition Reaction:The reaction In which a compound split into two or more simple substances is called decomposition reaction.
A→B+C
Thermal Decomposition:When decomposition is carried out by heating.
Eg (i) 2FeSo⁴(s)→FeO³(s)+SO²(g)+SO³(g)
(ferrous sulphate) (ferric oxide)
Green colour Red-brown colour
(ii)CaCo³(s) →Coa(s)+Co²(g)
(lime stone) (Quick lime)
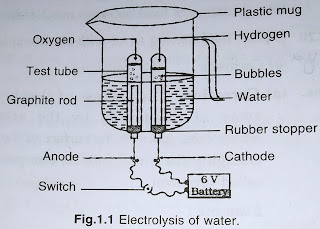
Eg 2H²O electric current 2H²+0²
————————>
Photolytic Decomposition:when decomosition is carried out in presence of sunlight.
Eg 2AgCl(s) Sunlight 2Ag(s)+Cl²(g)
————>
2AgBr(s) sunlight 2Ag(s)+Br²(g)
—————>
• Above reaction is used in black and white photography.
Endothermic Reaction:The chemical reaction in which require energy in the form of heat, light or electricity to break reactants are called endothermic reactions.
Displacement Reaction:The chemical reaction in which more reaction element displaced less reactive element from its salt solution.
Fe(s)CuSO⁴(aq)→FeSO4(aq)+Cu(s)
The iron nail become brownlish in colour by deposition of Cu and blue colour of CuSo⁴ changes to directly green colour due to formation of FeSo⁴.
Zn +CuSo⁴→ZnSo⁴+Cu
Zn is more reactive than copper.
Double Displacement Reaction:A reaction in which new compounds are formed by mutual exchange of ions between two Compounds.
Na²SO(aq)+BaCl(aq)→BaSo⁴(s)+2Nacl(aq)
White precipitate of BaSo⁴ is formed, so it is also called precipitation reaction.
Oxidation and Reduction:
Oxidation:(i)The addition of oxygen to reactant.(ii)The removal of hydrogen from a reactant.
C+O²→Co²
2Cu+O² heat 2Cuo
———>
Cuo+H² heat Cu+H²O
———>
Reduction:(i)The addition of hydrogen to reactant.(ii)The removal of oxygen from a reactant.
In this reaction Cuo is reduced to Cu and H² is oxidized to H²O.So, Oxidation and reduction taking place together is redox reaction.
Affects of oxidation in Daily life
Corrosion: when a metal is attacked by substances around it such as moisture , acid, etc.it is said to corrode and this process is called corrosion.
Example of corrosion:-
The black coating on silver and the green coating on copper are example of corrosion , Rusting of iron etc.
Note:Gold and silver do not corrode in moist air because these are noble metals and are not attacked by air and moisture.
•Corrostion causes damage to car bodies, bridges, iron railings, ships and to all objects made of metal , specially those of iron.
•Corrosion of iron is a serious problems.Every year an enormous amount of money is spent to replace damaged iron.
Here are some steps to prevention iron objects from corrode.
•Corrosion can be prevented by galvanization.
•Electroplating
•By putting paints.
Rancidity:The oxidation of fats and oils when exposed to air is know as rancidity.it lead to bad smell and bad taste of food.
Method to Prevent Rancidity
(I)By adding antioxidants.
(II)Keeping food in air tight containers.
(III)Replacing air by nitrogen.
(IV)Refrigeration.
In-Text Questions (Page 6, 10, 13, 14)
Q1. Why should a magnesium ribbon be cleaned before burning in air?
Answer:
Magnesium ribbon should be cleaned before burning to remove the protective layer of magnesium oxide that forms on its surface when exposed to air. This layer prevents it from burning effectively. Cleaning helps it react more efficiently with oxygen.
Q2. Write a balanced chemical equation for the following reactions:
- (a) Hydrogen + Chlorine → Hydrogen chloride
- (b) Barium chloride + Aluminium sulphate → Barium sulphate + Aluminium chloride
- (c) Sodium + Water → Sodium hydroxide + Hydrogen
Answer:
- (a) H2+Cl2→2HCl
- (b) 3BaCl2+Al2(SO4)3→3BaSO4+2AlCl3
- (c) 2Na+2H2O→2NaOH+H2
Q3. Write a balanced equation for the reaction between hydrogen sulphide and chlorine to give sulphur and hydrogen chloride.
Answer:
H2S+Cl2→S+2HCl
Q4. What is a balanced chemical equation? Why should chemical equations be balanced?
Answer:
A balanced chemical equation has an equal number of atoms for each element on both the reactant and product sides. Chemical equations must be balanced to follow the Law of Conservation of Mass, which states that matter cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction.
Exercise Questions (Page 13-14)
Q1. A solution of a substance ‘X’ is used for whitewashing. What is ‘X’? Write its reaction with water.
Answer:
‘X’ is calcium oxide (quicklime). When it reacts with water, it forms calcium hydroxide, which is used for whitewashing.
The reaction is:
CaO+H2O→Ca(OH)2
Q2. Why is the amount of gas collected in one of the test tubes in Activity 1.7 double of the amount collected in the other? Name this gas.
Answer:
In Activity 1.7, water decomposes into hydrogen and oxygen gas upon passing an electric current. Since the water molecule has two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom, the volume of hydrogen gas collected is double that of oxygen gas. The gas collected in larger quantity is hydrogen.
Q3. Why does the colour of copper sulphate solution change when an iron nail is dipped in it?
Answer:
When an iron nail is dipped in copper sulphate solution, iron displaces copper from copper sulphate because iron is more reactive than copper. This reaction forms iron sulphate, which is green in colour, causing the solution to change from blue to green.
The reaction is:
Fe+CuSO4→FeSO4+Cu
Q4. Give an example of a double displacement reaction and a precipitation reaction.
Answer:
Double displacement reaction:
AgNO3+NaCl→AgCl+NaNO3
Precipitation reaction:
BaCl2+Na2SO4→BaSO4(white precipitate)+2NaCl
Q5. Identify the substances that are oxidised and the substances that are reduced in the following reactions:
- (i) 4Na+O2→2Na2O
- (ii) CuO+H2→Cu+H2O
Answer:
- (i) Sodium (Na) is oxidised to Na2O.
- (ii) Copper oxide (CuO) is reduced to copper (Cu), and hydrogen (H₂) is oxidised to water (H₂O).
Q6. What is a redox reaction? Give an example.
Answer:
A redox reaction is a chemical reaction in which oxidation and reduction occur simultaneously. In this reaction, one substance loses electrons (oxidised), while the other gains electrons (reduced).
Example:
Zn+CuSO4→ZnSO4+Cu
In this reaction, zinc is oxidised, and copper is reduced.
Q7. Why do we apply paint on iron articles?
Answer:
We apply paint on iron articles to prevent rusting. The paint forms a protective layer that prevents moisture and oxygen from coming into direct contact with the iron, thereby preventing oxidation (rusting).
Q8. Oil and fat containing food items are flushed with nitrogen. Why?
Answer:
Oil and fat containing food items are flushed with nitrogen to prevent rancidity. Nitrogen, an inert gas, prevents the food from reacting with oxygen, which would otherwise lead to oxidation and spoilage of the food.
Q9. Explain the following terms with examples:
- (a) Corrosion
- (b) Rancidity
Answer:
(a) Corrosion:
Corrosion is the process by which metals are gradually eaten up by the action of air, moisture, or chemicals. For example, iron rusts when exposed to moisture and air, forming iron oxide (rust).
(b) Rancidity:
Rancidity is the process by which fats and oils get oxidised, leading to an unpleasant smell and taste. This commonly occurs in food items like chips and snacks when exposed to air for a long time.




.jpg)

0 Comments
Use the respectfully words in comment box.